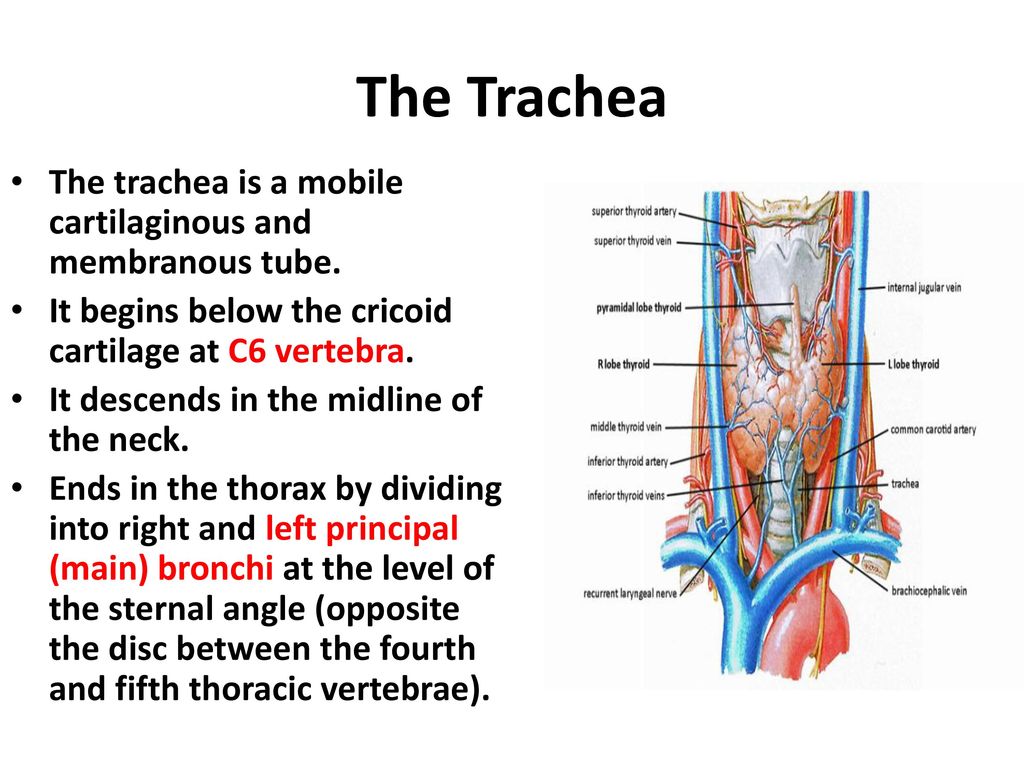
Describe the Structure of the Trachea
The vocal folds the vibrating part of our instrument are housed inside. It is made of incomplete rings of cartilage and smooth.

What Is Trachea Function Structure And Purpose Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Be able to recognize gastric glands identify their constituent cells.
. Structure of the Heart. The heart is enclosed in a pericardial sac that is lined with the parietal layers of a serous membraneThe visceral layer of the serous membrane forms the epicardium. Describe the structure and function of cartilage.
Sentence structure is how a sentence is put together including subjects verbs and. The major differences between the two systems are evident in the responses that each produces. The laryngeal structure is malformed and floppy causing the tissues to fall over the airway opening and partially block it.
The larynx is attached to one bone the hyoid bone which is the only floating bone in the body. The trachea returns those substances to the mouth through the act of coughing. This type of cartilage is predominately collagen yet with few collagen.
Air enters the body and is warmed as it travels through the mouth and nose. The trachea or windpipe serves to conduct air downward into the lungs. The bronchi bring air from the trachea into the lungs.
Describe the signaling molecules and receptor proteins involved in communication within the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system. The larynx is a series of cartilages that sits on top of the trachea or the windpipe. The process does not require the use of coagulation chemistry.
The nervous system can be divided into two functional parts. It also serves to protect the lungs from contamination such as gastric contents and blood. Cells have long been recognized as the simplest units of living matter that can maintain life and reproduce themselves.
This is the most common cause of noisy breathing in infancy. This is the term used to describe the tree-like structure of passageways that brings air into the lungs. The trachea divides into two bronchi.
Simple epithelium can be divided into 4 major classes depending on the shapes of constituent cells. A structure can be a skyscraper an outhouse your body or a sentence. Lab Content Introduction In contrast to epithelia connective tissue is sparsely populated by cells and contains an extensive extracellular matrix consisting of protein fibers glycoproteins and proteoglycans.
From its origin the subclavian artery travels laterally passing between anterior and middle scalene muscles with the anterior scalene scalenus anterior on its anterior side and the middle scalene scalenus medius on its posteriorThis is in contrast to the subclavian vein which travels anterior to the scalenus anteriorAs the subclavian artery crosses the lateral border of. This lets oxygen and CO2 pass easily between the alveoli and capillaries which are very small blood vessels. This system brings in oxygen and expels carbon dioxide and water.
Bronchi each leads to a lung. Layers of the Heart Wall. Electrospinning is a fiber production method that uses electric force to draw charged threads of polymer solutions or polymer melts up to fiber diameters in the order of some hundred nanometers.
It is also lined by tiny hairs called cilia and mucus producing cells that trap debris and foreign substances. They sit at the ends of the branches of your respiratory tree. The somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
Like the trachea they are also. Respiratory system consisting of the nose nasopharynx trachea and lungs. Skin capillary walls glomeruli pericardial lining pleural lining peritoneal.
The human heart is a four-chambered muscular organ shaped and sized roughly like a mans closed fist with two-thirds of the mass to the left of midline. The main function of the trachea is to funnel the inhaled air to the lungs and the exhaled air back out of the body. Be able to describe the layers in the wall of the digestive tract mucosa submucosa muscularis propria and adventitiaserosa and explain how they differ in the pharynx esophagus and stomach.
It is therefore a very mobile structure. The function of this type of tissue is to provide structural and mechanical support for other tissues and to mediate the. Building Although its certainly used to describe buildings it can do more than that.
Hyaline cartilage is the most widespread cartilage type and in adults it forms the articular surfaces of long bones the rib tips the rings of the trachea and parts of the skull. Laryngomalacia is a congenital softening of the tissues of the larynx voice box above the vocal cords. The trachea splits into a left and right bronchus plural.
Know the histological differences in the pharynx and the upper middle and lower portions of the esophagus. A familys structure includes the relationship of its members your body structure can refer to how your muscles and bones fit together. This system brings in oxygen and expels carbon.
The human body is a single structure but it is made up of billions of smaller structures of four major kinds. It then enters the trachea. The endotracheal tube ETT was first reliably used in the early 1900s1 In its simplest form it is a tube constructed of polyvinylchloride PVC that is placed between the vocal cords through the trachea to provide oxygen and inhaled gases to the lungs.
The walls of the alveoli are very thin. Bronchiole Each bronchus splits again and again into thousands of smaller tubes called bronchioles which. The human body which is made up of numerous cells begins as a single newly fertilized cell.
The human trachea is a cylinder about 25 to 30 cm 98118 in long which sits in front of the esophagus and extends from the pharynx into the chest cavity to the lungs. One cubic millimeter of lung tissue contains around 170. Electrospinning shares characteristics of both electrospraying and conventional solution dry spinning of fibers.
The cells found in this epithelium type are flat and thin making simple squamous epithelium ideal for lining areas where passive diffusion of gases occurAreas where it can be found include.
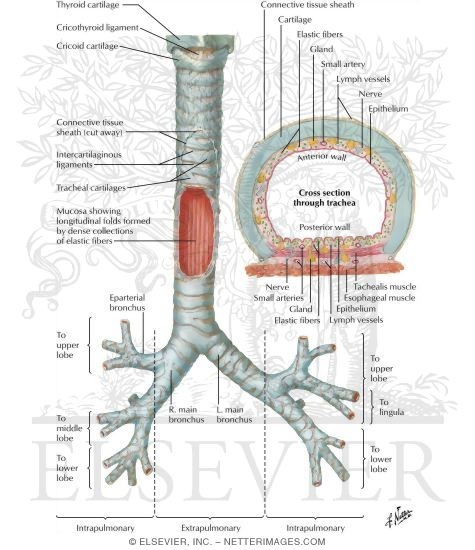
Structure Of The Trachea And Major Bronchi

Objectives Discuss The Anatomical Structure Of The Trachea With Its Relations Define The Term Bronchial Tree Describe Bronchopulmonary Segments Ppt Download
Comments
Post a Comment